EKS Auto and Karpenter with VPC secondary IP




AWS VPC supports secondary CIDR range that can be assigned to EKS pods. This means that we can have a smaller routable CIDR range for nodes while having a secondary IP range for pods networking.
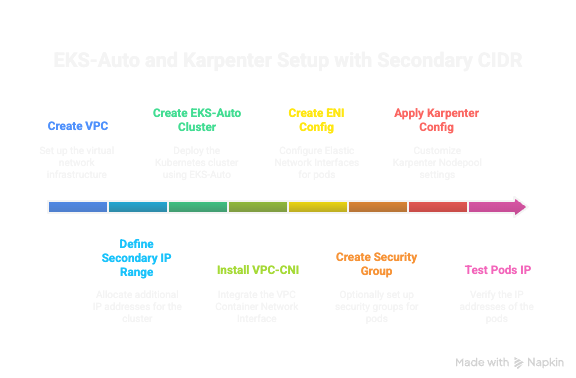
In order to provision pods in secondary IP range with EKS-Auto, you must create/update following
- Install/Update VPC-CNI package with
custom networkingenabled - Create ENI config for each subnets in each zone
- Custom Karpenter NodeClass and NodePool with higher priority than default nodepool
Source Code:
Complete setup
In thins example, I will create a VPC with Primary CIDR range of 10.0.0.0/24 spready across 3 AZ and subnets. Will create secondary CIDR in range of 100.0.0.0/16
**Applying the code **
terraform init -upgrade
terraform apply
# Once EKS is ready, update config
aws eks --profile labs --region eu-west-1 update-kubeconfig --name eks-auto-demo
kubectl cluster-info
# Apply new custom nodepool
kubectl apply -f Bootstrap/cni-nodepool.yaml
# Create a pod and validate they are assigned with secondary IP
kubectl run nginx --image=nginx
Step 1. Create VPC
Create VPC as normal with necessary CIDR range. VPC module does support secondary IP, however I am creating it separate so that custom tags can be added.
Step 2. Define secondary IP range
# Create secondary CIDR once VPC is created
resource "aws_vpc_ipv4_cidr_block_association" "secondary_cidr" {
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
cidr_block = local.secondary_cidr_block
}
resource "aws_subnet" "podnet" {
for_each = {
for idx, az in local.azs :
az => {
cidr_block = local.pod_subnets[idx]
}
}
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
availability_zone = each.key
cidr_block = each.value.cidr_block
tags = {
"Name" = "${module.vpc.name}-pod-subnet${each.key}"
"kubernetes.io/role/internal-elb" = "1" # Tag for internal LoadBalancer
"kubernetes.io/role/cni" = "1"
"pod_subnet" = "true"
"subnet_purpose" = "EKS_Cluster"
}
depends_on = [aws_vpc_ipv4_cidr_block_association.secondary_cidr] # Ensure VPC CIDR is created before subnets
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "podnet-association" {
for_each = aws_subnet.podnet
subnet_id = each.value.id
route_table_id = module.vpc.private_route_table_ids.0
}
Step 3. Create EKS-Auto cluster
module "eks" {
source = "terraform-aws-modules/eks/aws"
version = "21.0.6"
name = "eks-auto-demo"
kubernetes_version = "1.33"
# Optional
endpoint_public_access = true
# Optional: Adds the current caller identity as an administrator via cluster access entry
enable_cluster_creator_admin_permissions = true
compute_config = {
enabled = true
node_pools = ["general-purpose"]
}
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
subnet_ids = module.vpc.private_subnets
tags = {
Environment = "dev"
Terraform = "true"
Owner = "D Vettom"
}
}
Step 4. Install VPC-CNI and create ENI config per pod subnet
Must enable custom networking, and prefix deligation. Also update configs for creating ENI config per pods subnet/AZ
locals {
az = [for k, v in aws_subnet.podnet : v.availability_zone]
subnet_id = [for k, v in aws_subnet.podnet : v.id]
}
resource "helm_release" "vpc-cni" {
name = "aws-vpc-cni"
namespace = "kube-system"
repository = "https://aws.github.io/eks-charts"
chart = "aws-vpc-cni"
version = "1.19.6"
values = [
<<-EOT
env:
AWS_VPC_K8S_CNI_CUSTOM_NETWORK_CFG: "true"
ENABLE_POD_ENI: "true"
ENABLE_PREFIX_DELEGATION: "true"
ENABLE_SUBNET_DISCOVERY: "true"
eniConfig:
# Specifies whether ENIConfigs should be created
create: true
region: "${data.aws_region.current.region}"
subnets:
"${local.az[0]}":
id: "${local.subnet_id[0]}"
securityGroups:
- "${module.eks.node_security_group_id}"
"${local.az[1]}":
id: "${local.subnet_id[1]}"
securityGroups:
- "${module.eks.node_security_group_id}"
"${local.az[2]}":
id: "${local.subnet_id[2]}"
securityGroups:
- "${module.eks.node_security_group_id}"
EOT
]
}
Step 5. (Optional) Create SG for Pods network
You can create custom security group or use same as Clusters Security group
resource "aws_security_group" "pods_sg" {
name = "eks-auto-secondary-pods-sg"
description = "Security group for EKS Auto Pods using secondary IP address"
vpc_id = module.vpc.vpc_id
tags = {
Name = "eks-auto-secondary-pods-sg"
pod_security_group = "true"
purpose = "SG for Pods using secondary IP address"
}
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["10.0.0.0/8", "100.0.0.0/8"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["10.0.0.0/8", "100.0.0.0/8"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 1025
to_port = 65535
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["100.0.0.0/8"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 53
to_port = 53
protocol = "udp"
cidr_blocks = ["100.0.0.0/8"]
}
}
resource "aws_vpc_security_group_egress_rule" "allow_all_traffic_ipv4" {
security_group_id = aws_security_group.pods_sg.id
description = "Allow all outbound traffic"
cidr_ipv4 = "0.0.0.0/0"
ip_protocol = "-1" # semantically equivalent to all ports
}
Step 6. Apply custom Karpenter Nodepool config
Create a custom nodeClass with securityGroupSelectorTerms and podSecurityGroupSelectorTerms. Both can be same but ideal use dedicated. Update NodeClass with podSecurityGroupSelectorTerms and podSubnetSelectorTerms
Nodepool must refer to custom nodeClass and have a weight of more than 0 to take precedence over default nodepool provisioned by EKS-Auto
NodeClass must include securityGroupSelectorTerms, podSecurityGroupSelectorTerms, subnetSelectorTerms and podSubnetSelectorTerms. You must also ensure that all the subnets selected for EKS node must have corresponding podsubnet and ENI configuration available.
[!INFO] Configure Nodepool to provision NITRO instances, as Xen does not support CNI prefix-delegation
apiVersion: eks.amazonaws.com/v1
kind: NodeClass
metadata:
finalizers:
- eks.amazonaws.com/termination
name: primary-nodeclass
spec:
ephemeralStorage:
iops: 3000
size: 80Gi
throughput: 125
networkPolicy: DefaultAllow
networkPolicyEventLogs: Disabled
role: AmazonEKSAutoNodeRole
securityGroupSelectorTerms:
- tags:
"Name": "eks-auto-demo-node"
podSecurityGroupSelectorTerms:
- tags:
"Name": "eks-auto-demo-node"
snatPolicy: Random
subnetSelectorTerms:
- tags:
subnet_type: "private"
subnet_purpose: "EKS_Cluster"
podSubnetSelectorTerms:
- tags:
pod_subnet: "true"
subnet_purpose: "EKS_Cluster"
---
apiVersion: karpenter.sh/v1
kind: NodePool
metadata:
name: primary-nodepool
spec:
weight: 20
template:
spec:
expireAfter: 336h
nodeClassRef:
group: eks.amazonaws.com
kind: NodeClass
name: primary-nodeclass
requirements:
- key: "karpenter.k8s.aws/instance-hypervisor"
operator: In
values: ["nitro"]
- key: karpenter.sh/capacity-type
operator: In
values: ["spot","on-demand"]
- key: eks.amazonaws.com/instance-category
operator: In
values: ["c","m","r"]
- key: eks.amazonaws.com/instance-generation
operator: Gt
values: ["5"]
- key: kubernetes.io/arch
operator: In
values:
- amd64
- key: kubernetes.io/os
operator: In
values:
- linux
terminationGracePeriod: 24h0m0s
Test pods IP
Deploy a pond and verify that node IP is from private subnet and pods IP from pods subnet/secondary range